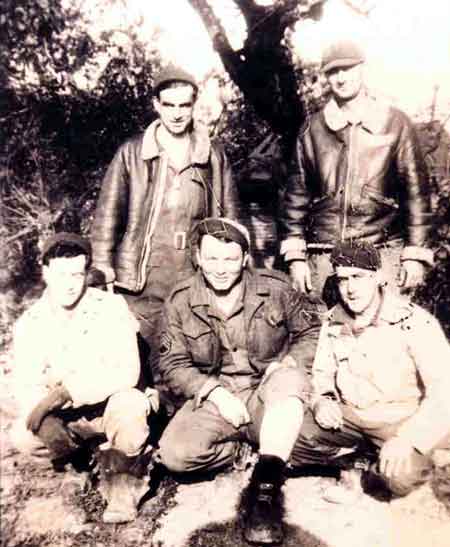
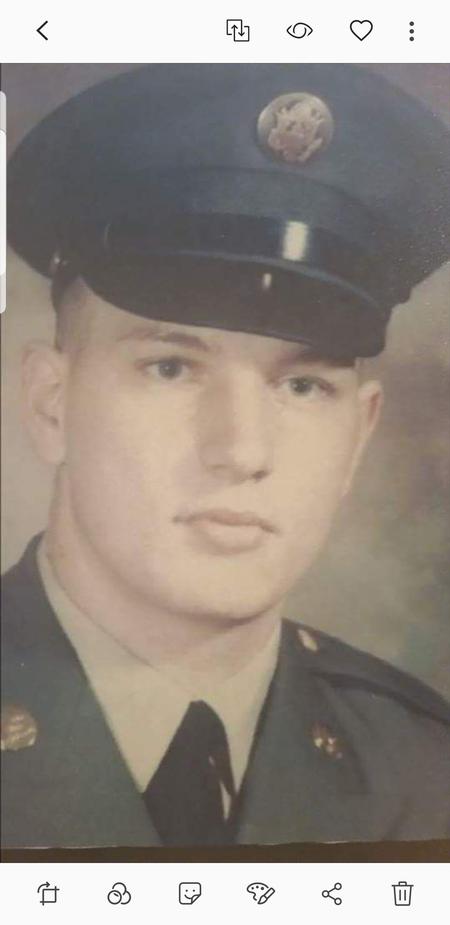
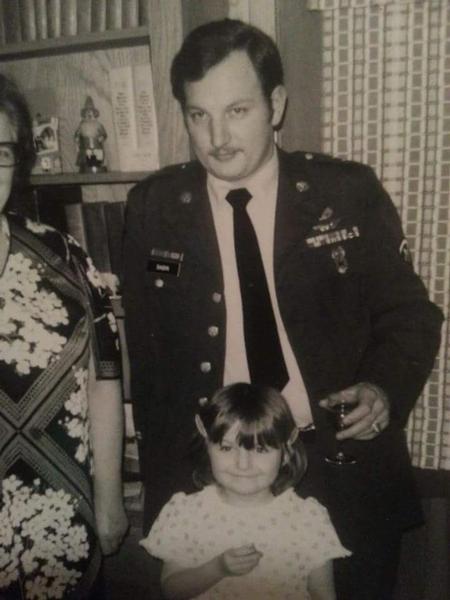
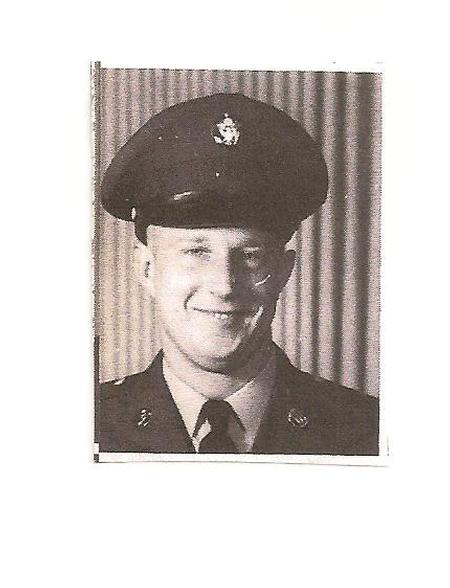
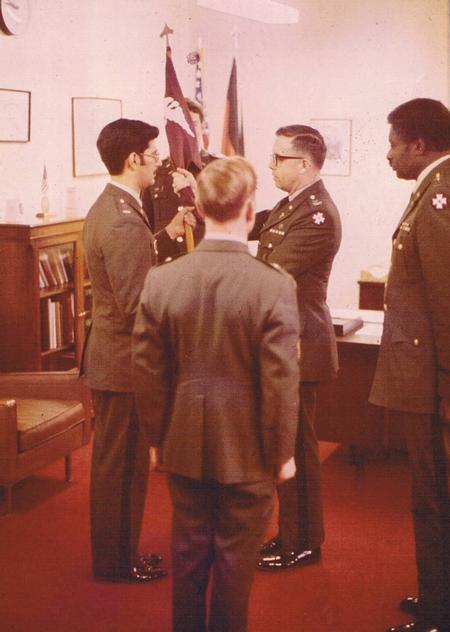
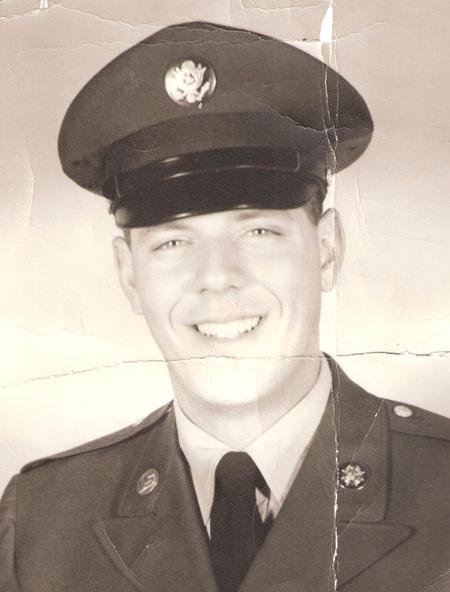
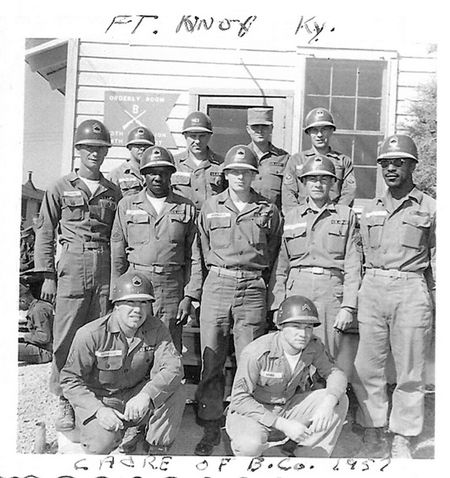
ABOUT Army Security Agency
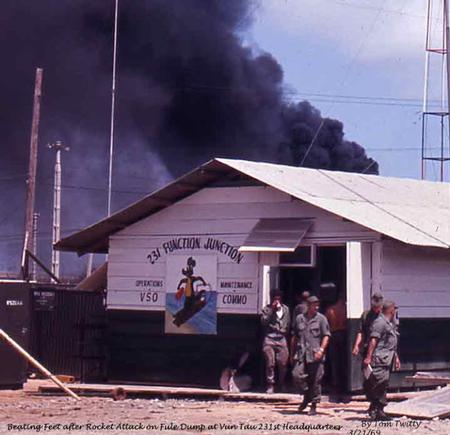
- During the Vietnam War, ASA intercepted and deciphered enemy communications, providing crucial intelligence to US forces.
- The ASA was established in 1945 as the Signal Security Agency, and later renamed Army Security Agency in 1949.
- ASA personnel were involved in Operation Ivory Coast, the famous raid on the Son Tay prison camp in North Vietnam in 1970 to rescue American prisoners of war.
- ASA played a key role in deciphering encrypted messages from the Soviet Union during the Cold War.
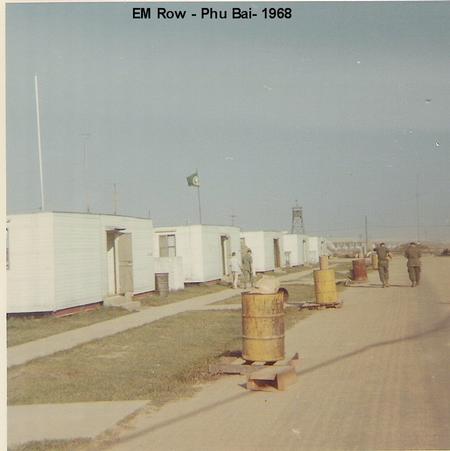
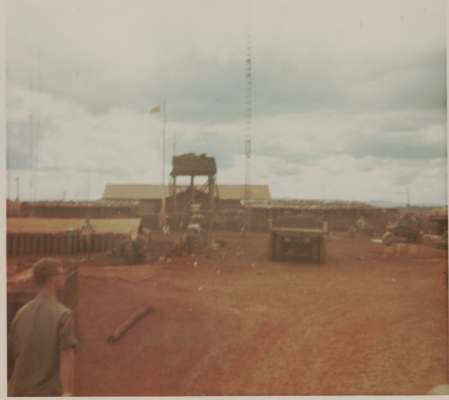
- The ASA had a network of listening posts around the world, including in Germany, Korea, and Vietnam.
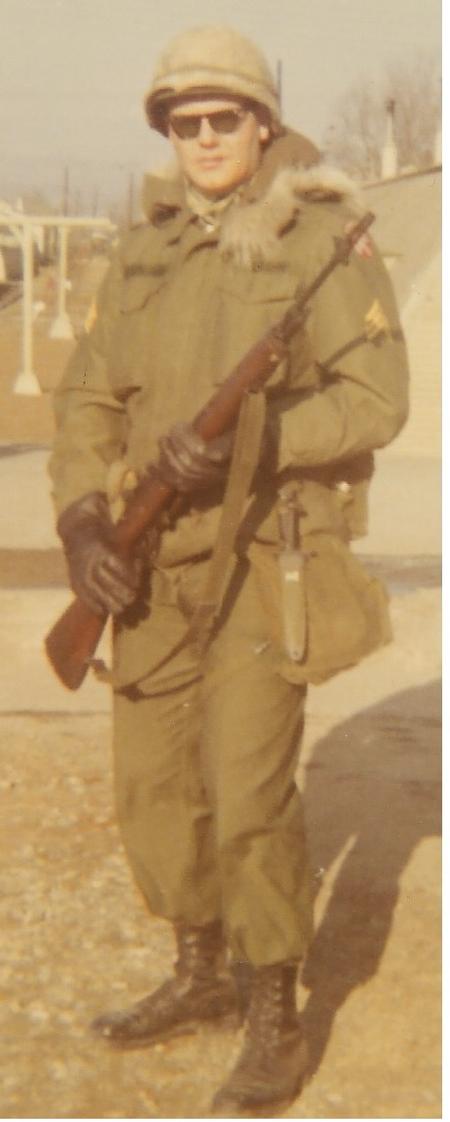
- ASA personnel were trained in Morse code, cryptography, and other forms of intelligence gathering.
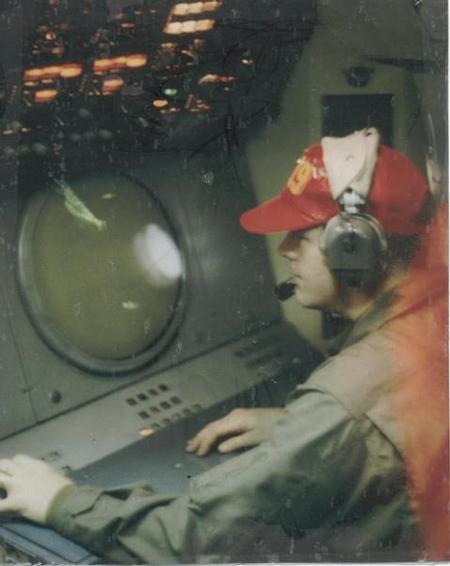
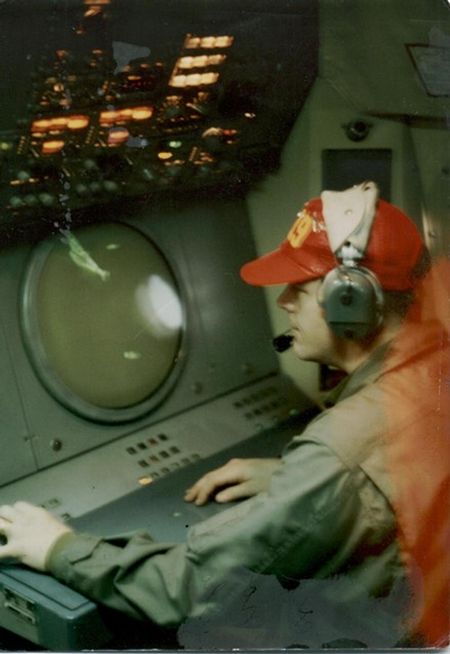
- ASA intercept operators worked around the clock, listening in on enemy communications and quickly translating them for military commanders.
- ASA linguists were skilled in multiple languages, including Russian, Korean, and Vietnamese.
- ASA cryptanalysts were responsible for breaking enemy codes, a vital part of the intelligence-gathering process.
- After the Vietnam War, the ASA was disbanded and its functions were absorbed by the National Security Agency.
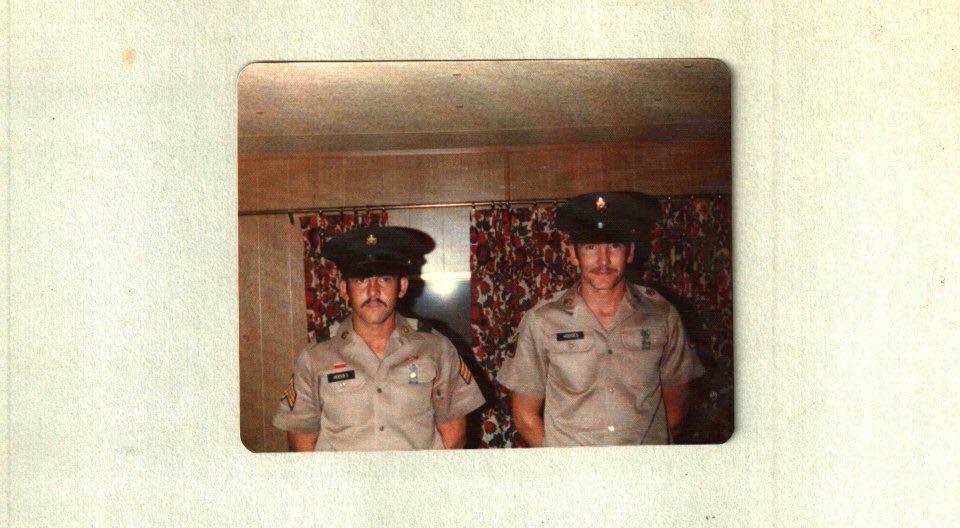







































































--42795.jpg)
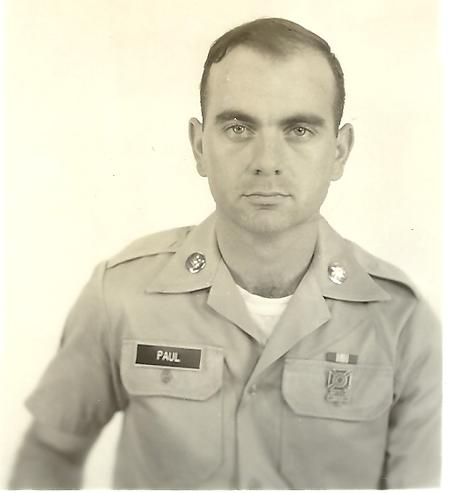
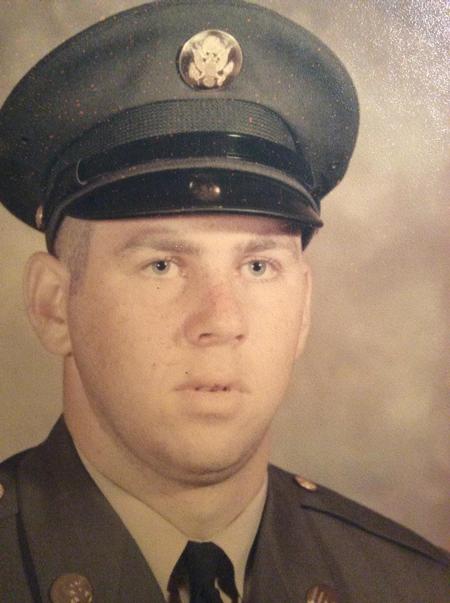
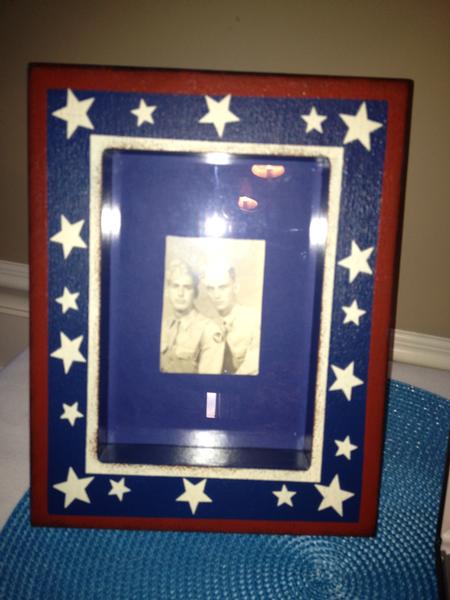
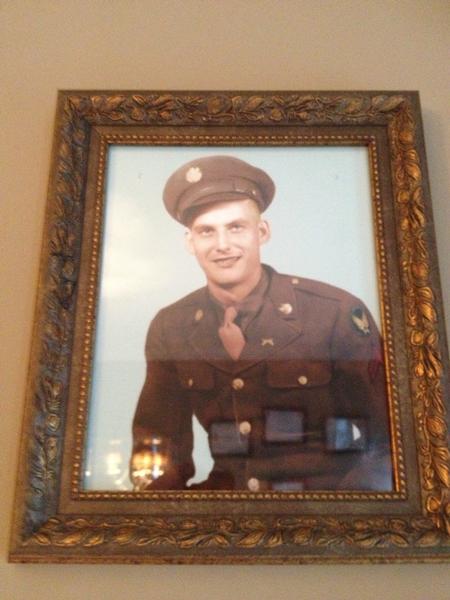




















































































-F-Sneathen-III--52139.jpg)





























































































--40617.jpg)
--74697.jpg)




















































































































































































































.jpg)